The driverless car market is just starting to emerge, but experts predict its rapid growth in the coming years. Let’s explore how the Internet of Things (IoT) is changing the automotive industry.
A number of the leading global automakers such as BMW, Audi, Volkswagen, General Motors and Toyota, together with IT-giants Google and Apple, place serious emphasis on autonomous driving and IoT technology. They are actively engaged in the development of automotive IoT solutions to assist drivers and, as the ultimate goal, to create a Level 5 (see below) self-driving car.
Start your IoT or embedded software development project with SaM Solutions to benefit from our technical expertise and ensure a timely launch.
Their collaboration has already had some impressive results. Audi AG, for example, claimed that the usage of the brake assist system in their vehicles in the last five years reduced the total number of passenger injuries by 38 percent.
Connected Cars Background
The track record of integrating vehicles and digital technology is really long and rich and may be considered to start in 1911, when automakers began installing the first piece of electronics in automobiles — electric starters.
In 1985, drivers saw in their cars the ancestor of infotainment systems — a compact disc player. Dashboard computer diagnostics appeared in 1994 and were followed by GPS navigation systems introduced in 1995.
A new millennium was marked by the introduction of USB and Bluetooth connectivity available for automobiles. Thus, in the 2000s, car producers got very close to the creation of IoT cars.
A research service BI Intelligence predicted more than 94 million connected cars to be produced in 2021, which would represent a compound annual growth rate of 35 percent from 21 million smart vehicles shipped in 2016.

Levels of Driving Automation
The IoT technology can empower connected devices to perform some actions independently; that is, without human interference. To create a connected car, the Internet of Things introduces various features and smart options for a vehicle. The hierarchy of driving automation was outlined on the basis of the progression of these features.
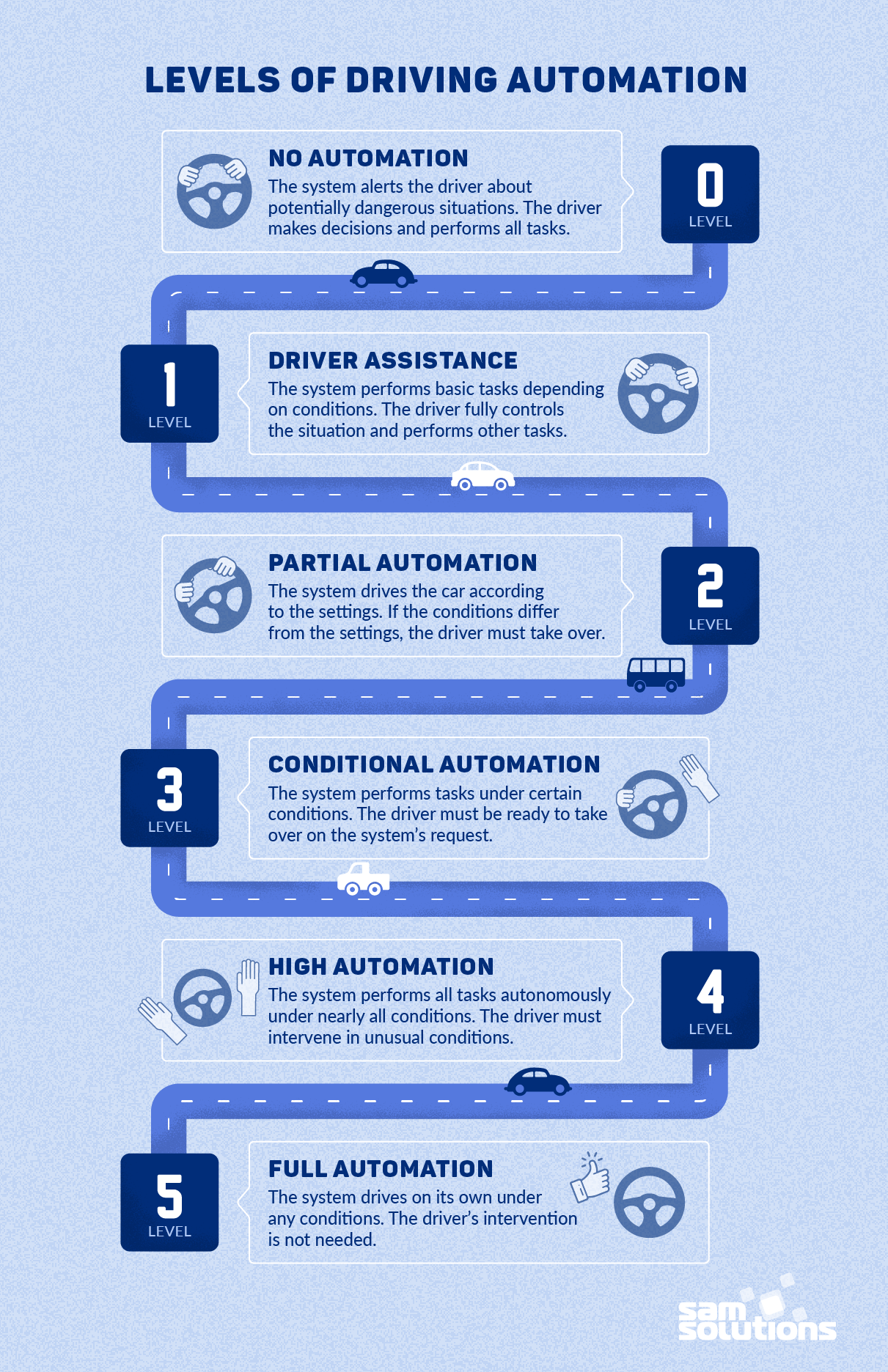
Level 0: No Automation
- The system alerts the driver about potentially dangerous situations
- The driver makes decisions and performs all tasks
Examples: regular cruise control
Level 1: Driver Assistance
- The system can automatically accelerate, steer and brake the car depending on driving conditions
- The driver must fully control the situation on the road and perform other tasks
Examples: adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assistance
Level 2: Partial Automation
- The system monitors and analyzes driving conditions and can perform multiple tasks, either for safety reasons or according to the driver’s commands
- The driver must fully control the situation on the road and take over in case the conditions don’t correspond with the system’s settings
- These are not fully self-driving cars: they can drive autonomously only under certain conditions.
Examples: Tesla Autopilot, Volvo Pilot Assist, Mercedes-Benz Drive Pilot, Cadillac Super Cruise
Level 3: Conditional Automation
- The system can perform all tasks in the autonomous driving mode under specific conditions (e.g. speed, traffic, time of day)
- The driver doesn’t have to continuously monitor the environment and can carry out other activities
- The driver must be ready to take over the driving tasks on the system’s request. It happens when the set conditions for Level 3 are exceeded (e.g. speed 37 mph) and the autonomous mode becomes challenging.
Examples: Audi A8
Level 4: High Automation
- The system will perform all tasks in the autonomous driving mode under specific conditions
- If the driving mode becomes challenging, the system will request the driver to take over the driving tasks. Nevertheless, it will be able to respond to challenging situations, if the driver doesn’t react promptly.
- There still will be pedals and a steering wheel, as the driver’s intervention will be needed in unusual environments
Examples: don’t exist yet
Level 5: Full Automation
- The system drives on its own under any conditions
- The driver’s intervention is not needed
Examples: don’t exist yet
Currently, all vehicles that have some autonomous components fall under Level 1 and Level 2 and focus on assisting drivers. The highest level of car autonomy that has been reached by now is Level 3 with the only representative — Audi A8 — announced in July 2017.
Remember, no self-driving car that falls into categories of high or full automation currently exists! Drivers are still responsible for their behavior on the road.
IoT in Connected Cars: General Working Principles
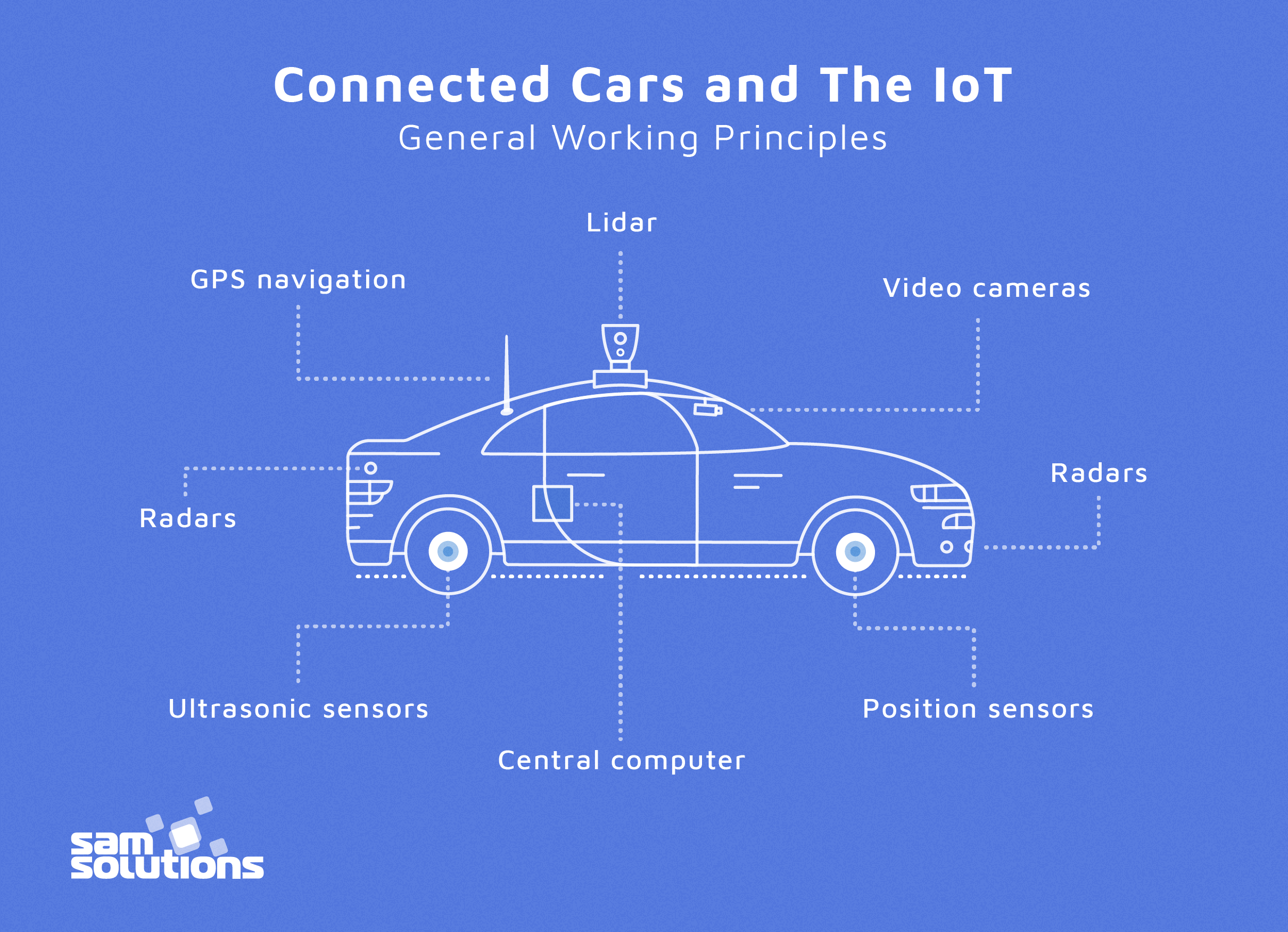
Autonomous cars have roughly the same components:
- Video cameras (forward, rear, side) — detect traffic lights and signals of other cars; read road signs; detect pedestrians, cyclists and obstacles; provide 360 degrees of visibility around the car.
- Radars (forward, rear) — detect objects and their velocities at long distances; are able to see the car ahead through heavy rain, fog and dust; monitor the position of other vehicles nearby; measure the distance to objects and help to park.
- Lidar — a rotatable radar on the roof that scans the environment up to 100 meters and creates a 3D map of the location.
- Ultrasonic sensors — complement the vision, detecting hard and soft objects, and measuring the position of objects close to the vehicle.
- Position sensors — may be built in the wheels to sense their movements and detect the car position on the map.
- GPS navigation — catches signals from satellites to provide more accurate positioning.
- Central computer — provides analytics of the gathered data and influences decision-making.
The software and algorithms for autonomous cars must be extremely powerful in order to process the info from the extended network of sensors and make the right decisions. Vehicles should literally learn communication skills to be able to see, hear and interpret any situation on the road. Moreover, the system should be able to predict the behavior of people both in and out of the car and correct it for the sake of safety.
High-quality mapping is a good supplement to the above-mentioned devices and can greatly improve the autonomous driving experience. The modern mapping industry might boom in the near future.
IoT Self-Driving Cars: Advantages and Challenges
It’s hard to say definitively how IoT applications in the automotive industry will affect humanity. Most developers tend to believe that connected cars and the IoT will revolutionize the existing transportation system. But will the changes be more negative or positive? Take a look at the possible pros and cons of implementing IoT in automotive manufacturing.
Advantages
- People with poor eyesight and other health problems will be able to move around in personal Internet of Things cars
- Accidents on the roads and the number of human fatalities and injuries will be reduced to a minimum
- The delivery of goods to remote or devastated areas will be simplified, and drivers will not risk their lives
- Companies will reduce delivery costs by saving on driver salary, and due to more economical fuel consumption or electric cars usage
Challenges
- Legislative issues, as it’s hard to identify those responsible for damage
- A person may lose the right to drive
- Professional drivers will lose their jobs
- 100% reliable software is needed to avoid technical mistakes
- It’s hard to protect an IoT auto from cyber attacks and external interference
- The ethical issue: how an IoT vehicle will rationally choose a behavior model in an inevitable collision (e.g., to hit a pedestrian or to drive a car off the road where passengers may die)
Automotive IoT Use Cases
Despite the fact that autonomous vehicles are not yet available, many companies in different countries are actively testing them in real conditions.
In 2016, Dubai authorities launched the self-driving bus and tested it along the city streets for a route of about 700 meters.
An autonomous taxi service also appeared in Dubai. It started with 50 Tesla cars, each equipped with Tesla’s latest Autopilot software. Actually, Dubai authorities plan to automate 25% of the city’s transport by 2030.
In March 2018, in Japan, Nissan Motor and a mobile games producer DeNa started testing the self-driving taxi service EasyRide they developed together.
Passengers use an application to call for a taxi that delivers them to predetermined destinations in the city. An in-car tablet screen provides information about local sightseeing areas. After the ride, passengers complete a survey: they share their experience and suggest the possible price they would pay for EasyRide when it’s officially launched.
Google’s autonomous car development company Waymo has tested its cars in California, Texas, Washington, Nevada, Michigan and Arizona. In 2018, the next stop for the test program will be Atlanta, Georgia.
The Future of Transportation
IoT for the automotive industry has become a must. According to the latest forecasts of the Boston Consulting Group (BCG), the total volume of the unmanned vehicle market may be sized at about $42 billion by 2025. It is expected that the share of self-driving cars in the global sales structure will reach 12-13 percent. In other words, about 14 million autonomous cars will be launched on the market.
McKinsey Global Institute is even more optimistic in its forecasts, assuming that the total share of unmanned vehicles (both fully autonomous and semi-autonomous) will reach 15-20 percent by 2025.
By some estimates, in just a few decades, IoT in car manufacturing will allow mankind to save about $1 trillion in total and provide a 70 percent reduction in the number of fatal accidents. Even now, automation significantly reduces the accident rate.
Many experts rightly believe that the biggest problem preventing driverless technology from developing is the imperfection of the legislative framework, rather than the lack of new technologies and solutions. However, there is progress in this direction. The US Department of Transportation issued its first recommendations regarding autonomous vehicles. AT Kearney consulting company predicts that the legal framework for unmanned vehicles will be fully developed by 2025.
However, it should be noted that people themselves are not ready for the active expansion of self-driving transportation yet. People must get used to the fact that their vehicles will be controlled by an automated system. That’s why transportation is going to experience gradual shifts.
What We Offer
SaM Solutions has significant experience in IoT and embedded development. Our specialists are able to provide:
- Full-cycle firmware development service for any IoT device
- Middleware solutions
- Custom P2M interfaces to operate IoT devices
- End-user applications
Contact us to learn more about our expertise in smart home technologies, industrial IoT, biometric security, embedded software development and more.



















 The Latest 15 Information Technology Trends in 2024
The Latest 15 Information Technology Trends in 2024 Top 10 Embedded Software Development Tools
Top 10 Embedded Software Development Tools IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS: What’s the Difference?
IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS: What’s the Difference? 10 Examples of Predictive Analytics
10 Examples of Predictive Analytics











 Top IoT Industry Trends in 2025
Top IoT Industry Trends in 2025 Java Web App Security: Everything You Need to Know
Java Web App Security: Everything You Need to Know Top 10 Latest Trends in the Ecommerce Industry in 2025
Top 10 Latest Trends in the Ecommerce Industry in 2025 Java Integration Testing: A Step-by-Step Guide
Java Integration Testing: A Step-by-Step Guide SAP Commerce Cloud (ex. Hybris) Implementation Guide
SAP Commerce Cloud (ex. Hybris) Implementation Guide
Pleasant post, Thank you for sharing profitable data. I appreciated perusing this post. The entire blog is extremely pleasant discovered some well done. Thanks for sharing.
The applications of IoT technology in vehicles vary from navigation and telematics solutions to infotainment and predictive maintenance systems. I guess that driver-assistance systems are highly important and must be installed in every car as they can prevent accidents on the road.
I like your detailed explanation and informative infographics. As for IoT in automobiles, this niche has a huge potential. More and more companies will implement IoT devices in their vehicles to ensure real-time monitoring and improve efficiency.
Video cameras, sensors, GPS navigation — these are widespread applications of IoT in vehicles. I’m sure that this segment will expand further at a rapid pace.
Will we ever see self-driving cars on our roads? Of course! Automotive companies leverage the Internet of Things technology to the fullest, so all cars will be connected soon.
Currently, IoT is one of the pillars of the automotive industry, since each modern car is equipped with smart connected devices that improve the security of driving.
Great writing style in this. Easy to understand.
Thanks! I’ll take a look.