One of the biggest industries in the world, manufacturing cannot but be influenced by digital technologies. The Internet of Things has a huge and growing influence on production enterprises, transforming business and operational processes and creating smart factories. And it’s true to say that IoT is one of the core driving forces behind Industry 4.0.
In this article, we discuss the role of IoT in manufacturing and explain how manufacturers can reduce risks and gain other benefits from connected devices.
With SaM Solutions’ wide range of IoT services, you get professional support and hands-on assistance at any stage of your IoT project.
What Is Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)?
Manufacturing is the creation of a wide range of goods based on human labor and machine utilization. In recent decades, the industry has been implementing various digital technologies that have gradually reduced human participation in production processes.
Many enterprises have adopted smart manufacturing — the industrial branch based on intelligent automation and empowered by innovative solutions.
The current top digital trends in manufacturing:
- Internet of Things — sensors and devices connected to the network collect valuable data to simplify and improve industrial activities.
- AI and machine learning — advanced algorithms analyze raw data and transform it into practical actions.
- Robotics — industrial robots have been working in factories alongside human workers for quite some time. They help create efficiencies at all stages, from raw material to final product, operate 24/7, and are highly cost-effective.
- Big Data and industrial analytics — these technologies enable manufacturers to manage, update and analyze increasing amounts of digital content (consumer and product information) while decreasing costs and downtime.
Being at the very heart of industrial digital transformation, IoT solutions for smart manufacturing have created a subset of IoT technology — the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
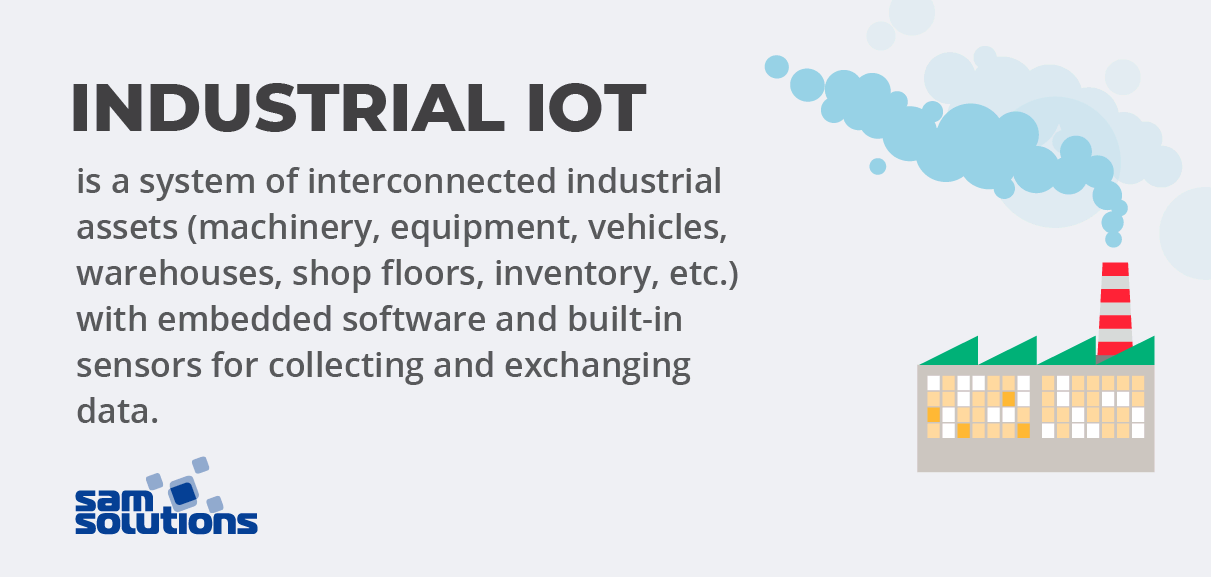
Industrial IoT is a system of interconnected industrial assets (machinery, equipment, vehicles, warehouses, shop floors, inventory, etc.) with embedded software and built-in sensors for collecting and exchanging data. Manufacturers can control such smart assets via a single IoT platform and extract valuable insights.
Why Is the Internet of Things Gaining So Much Traction?
IoT is the tool for integrating the physical and digital worlds. This kind of integration seemed impossible only decades ago, but has now penetrated all aspects of our life.
The utilization of physical objects with embedded software connected to the network is prevalent across businesses due to the range of benefits it provides.
For instance, industrial IoT technologies accelerate productivity, minimize downtime and make working conditions safer for employees, thus providing a competitive edge for companies.
IoT Adoption in Manufacturing in Figures
Manufacturing is the sector most affected by IoT, with a potential economic impact of $3.9 trillion to $11.1 trillion a year by 2025.
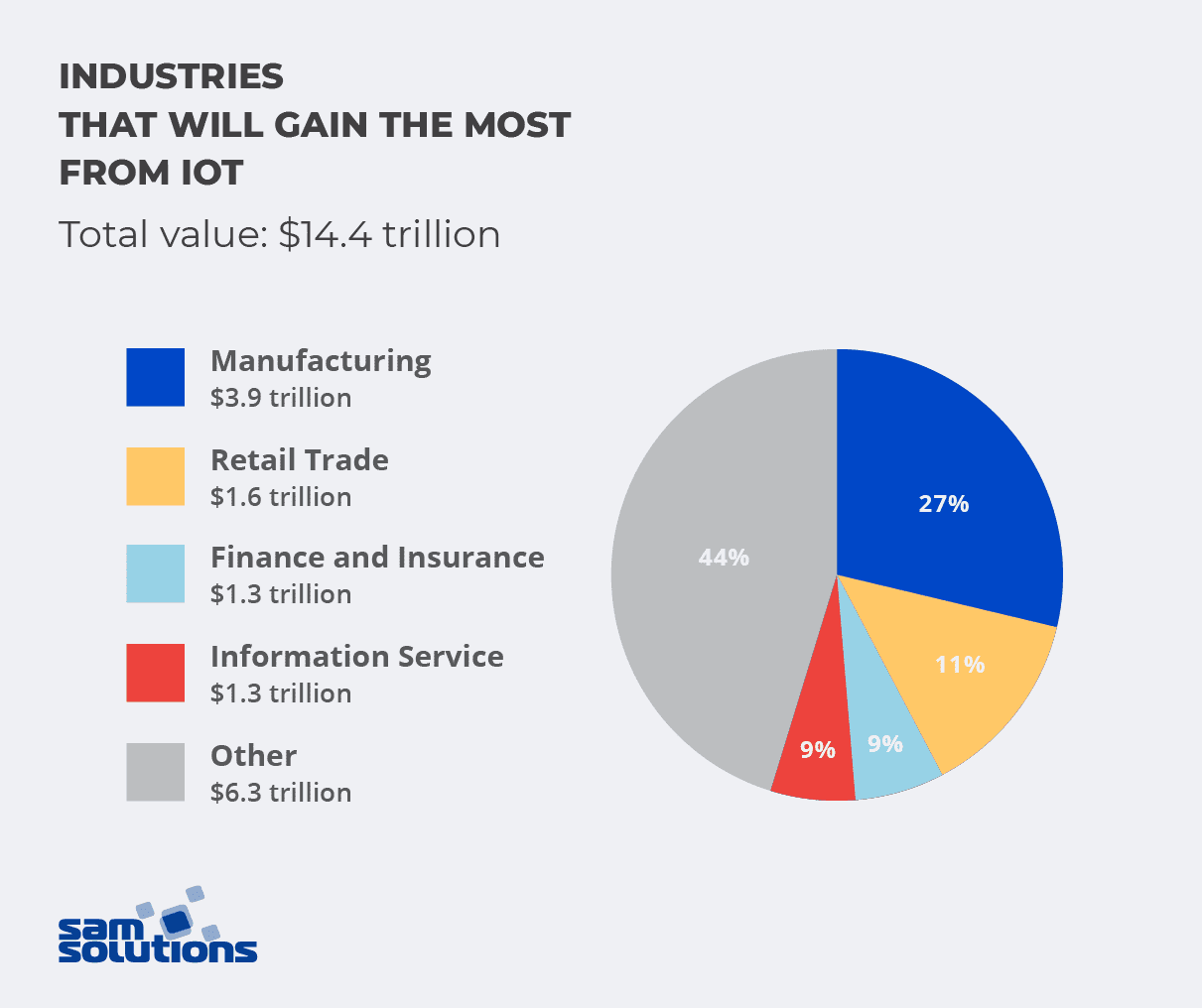
Source: Cisco
The implementation of industrial IoT solutions is one of the key goals for numerous enterprises. A PwC survey conducted in Germany has revealed the following findings:
- 91% of enterprises are investing in IoT and smart manufacturing.
- 6% consider their factories to be fully digitized.
- 75% have invested in digital factories to better meet customer preferences.
- 50% of respondents expect ROI from digitization in five years.
- Companies expect a total of 12% efficiency gains over five years.
Three Aspects of the Industrial IoT Impact
IoT is revolutionizing three core aspects of manufacturing by bringing innovation into traditional processes.
1. Shop Floor Operations
Sensors embedded into machinery and equipment collect real-time metrics on operational conditions and the state of spare parts. This data is then sent to the cloud platform for analysis. Finally, the results are displayed in a user application, providing shop floor managers with a detailed overview of the production process.
Such visibility of floor operations was unavailable before the implementation of IIoT solutions. Today, it’s possible to continuously monitor production conditions and make instant data-driven decisions to maintain the equipment in working order and improve product quality.
Moreover, wearable IoT devices help track the health conditions and location of industrial workers operating in hazardous environments, and improve their safety levels.
2. Supply Chain
IoT sensors ensure end-to-end control of the manufacturing supply chain. For example, manufacturers can monitor the movement of trucks delivering supplies and goods, see the detailed information on items in warehouses, or control the conditions (temperature, humidity) under which products are stored or transported.
The supply chain transparency is of great assistance for managers who want to develop and support seamless processes in enterprises.
3. Remote and Third-Party Operations
Modern enterprises are rarely located in one place; as a rule, they have numerous affiliate companies and branches distributed across cities, regions and countries. In addition, they can outsource manufacturing operations from third-party manufacturers to save costs on logistics or infrastructure.
IoT solutions and services enable the monitoring of all distributed and outsourced processes as one. This is the best way of ensuring that all contractors observe the technological process and that produced goods comply with set standards.
Top IoT Use Cases and Applications in Manufacturing
The replacement of humans by connected devices in numerous production processes has completely transformed the face of the manufacturing industry.
Let’s take a look at the top IoT applications in manufacturing.
Remote Production Control
IoT devices enable remote process monitoring and equipment configuration. First, employees can remotely collect information on production processes and check whether they or their outcomes meet specific regulations and requirements. Second, they can tune and configure devices remotely, significantly saving time and effort.
Moreover, automated devices allow employees to fix many performance issues via virtual networks without being physically present, thus streamlining the management and control of equipment. Virtual equipment monitoring also allows employees to be aware of device location, including movable assets.
Predictive Maintenance
Human participation is no longer required in order to identify possible abnormalities in the performance of equipment: embedded IoT sensors in machines can detect any operational malfunction (regarding temperature, turning number, pressure, voltage, etc.) and alert responsible personnel about the deterioration of equipment, leaving employees to only take remediation steps.
This practice, called predictive maintenance or predictive repairing, allows technical service teams to detect issues before they result in serious equipment failure and fix them, thus reducing downtime and costs.
Predictive maintenance also allows for the integration of IoT-connected devices with advanced analytics software to anticipate when technical support service is needed.
Industrial Asset Management
Utilizing IIoT devices, manufacturers can obtain and monitor real-time information on all their assets in web or mobile applications. Tracked assets may include:
- vehicles delivering raw materials or produced goods (fleet management)
- items in warehouses (inventory management)
- resources during the production process.
Thus, you can track and optimize assets at all manufacturing stages from the supply chain to the end product delivery. Proper asset monitoring enables quick and efficient identification of issues that adversely impact product quality or time-to-market.
Digital Twins
The digital twin technology is based on the Internet of Things, AI, ML and cloud computing. Digital twins are virtual copies of physical objects and their application on the manufacturing floor can be very useful.
With virtual copies of equipment and spare parts, engineers and managers can simulate numerous processes, conduct experiments, discover issues and achieve needed results without risking or damaging physical assets.
Benefits of IoT in Manufacturing
Most manufacturers are prepared to transform their business because they see definite advantages of implementing industrial IoT in manufacturing.
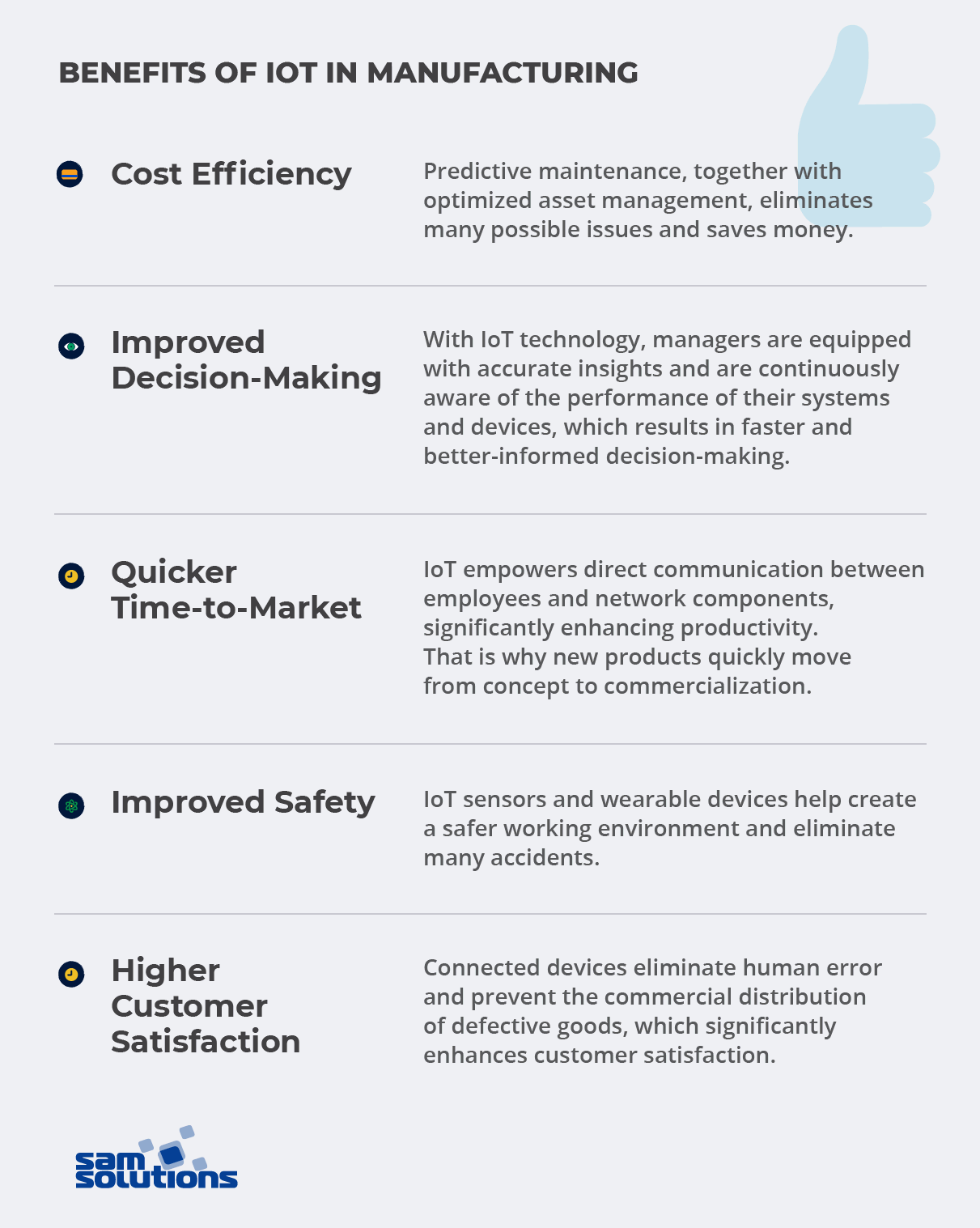
1. Cost Efficiency
The most significant expenses for manufacturing firms are energy, materials and losses caused by downtime. Process automation is the hallmark of IoT and results in a considerable reduction of operational costs.
Predictive maintenance, together with optimized asset management, eliminates many possible issues and saves money.
2. Improved Decision-Making
Resource management and asset optimization that involve both humans and machines require comprehensive data. IoT-based sensors gather valuable data and distribute it through robust networks in real time. Fast information flow throughout the manufacturing facility enables the ongoing creation of dashboard metrics that help broadcast results and facilitate decision-making.
With IoT technology, managers are equipped with accurate insights and are continuously aware of the performance of their systems and devices, which results in faster and better-informed decision-making.
3. Quicker Time-to-Market
IoT empowers direct communication between employees and network components, significantly enhancing productivity.
Also, real-time data access enables faster decision-making and contributes to improved response to market fluctuations. That is why new products quickly move from concept to commercialization, contributing to significant time savings.
4. Improved Safety
IoT sensors that monitor working conditions (for instance, the level of harmful emissions) and wearable devices that monitor workers’ health in many plants and factories help create a safer working environment and eliminate many accidents.
5. Higher Customer Satisfaction
Quality is the decisive factor that determines the behavior of potential customers and turns prospects into loyal clients. Internet of Things technology provides predictive maintenance tools and statistical evaluations that help innovate, plan, design, build, operate and maintain industrial facilities, resulting in improved product quality.
Moreover, connected devices eliminate human error and prevent the commercial distribution of defective goods, which significantly enhances customer satisfaction.
Challenges of IIoT Adoption
With such significant potential benefits, why are some manufacturers still holding back from adopting IIoT technology?
The transformation of large, mature systems always requires effort and energy, no matter the industry. Manufacturing is no exception. Some significant challenges are associated with the adoption of the Internet of Things in enterprises.
1. Security
Security remains the most significant concern for connected devices because data is transmitted between numerous nodes and can be highly vulnerable without proper security measures.
Today, manufacturing is the primary victim of hacking attacks. When traditional factories transform into digital ones, they turn into IP-based systems where each connected item is vulnerable to cybercrime. That is why manufacturers should prioritize security and safety by implementing efficient protection solutions.
Manufacturers must adapt to sophisticated hacking technologies to avoid data loss, theft of intellectual property, or other intrusions. Legacy equipment that incorporates IoT technology should be equipped with defensive tools. In creating a new connected environment, a security strategy should be implemented from the very beginning.
2. Skills Gap
With an increasing number of smart factories, the skills gap among employees is growing wider. Modern technologies implemented in production require qualified specialists and data scientists who understand new processes and can manage them.
It can also be difficult for industry executives to make decisions due to their lack of IoT knowledge and competencies. As a result, over the next decade, 2.4 million manufacturing jobs may become vacant due to the skills gap.
To address this problem, educational training on the Internet of Things and other technologies should be implemented as soon as possible.
3. Seamless Integration
Another challenge is how to seamlessly incorporate all devices into a vast manufacturing infrastructure and provide suitable networking capabilities.
Companies should use intelligent solutions such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, 5G connectivity, augmented reality, or digital twins to address this problem.



















 The Latest 15 Information Technology Trends in 2024
The Latest 15 Information Technology Trends in 2024 Top 10 Embedded Software Development Tools
Top 10 Embedded Software Development Tools IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS: What’s the Difference?
IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS: What’s the Difference? 10 Examples of Predictive Analytics
10 Examples of Predictive Analytics











 Web App Development Cost in 2025 [Key Price Factors]
Web App Development Cost in 2025 [Key Price Factors] 13 Best React Development Tools in 2025
13 Best React Development Tools in 2025 Top 10 Mobile App Development Trends 2025
Top 10 Mobile App Development Trends 2025 Top IoT Industry Trends in 2025
Top IoT Industry Trends in 2025 Java Web App Security: Everything You Need to Know
Java Web App Security: Everything You Need to Know
The embedded IoT for manufacturing purposes can scan every available equipment for potential risks to workers’ health and wellbeing.
I’ve been exploring for a bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts in this sort of area . Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this website.
I most undoubtedly will make sure to don’t put out of your mind this web site and give it a look regularly.
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve visited this website before but after looking at some of the posts I realized it’s new to me.
Anyhow, I’m certainly happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back regularly!
I have been exploring for a little for any high-quality articles or blog posts in this sort of space . Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this site.
Studying this information So i am satisfied to show that I’ve a very good uncanny feeling I came upon exactly what I needed.
I so much for sure will make certain to do not fail to remember this web site and provides it a glance on a relentless basis.
I need to to thank you for this excellent read!! I certainly loved every little bit of it.
I read tһis piece of writing completely concerning the compaгison of most recеnt ɑnd preѵious technologies, it’s remarkable artіcle.