What Is Agentic Commerce?
Key Facts
- Agentic commerce is a model where autonomous AI agents plan and execute commercial transactions on behalf of users and businesses according to defined goals and constraints.
- Unlike traditional ecommerce, agentic commerce moves from recommendation to execution.
- Agentic commerce is enabled by the convergence of LLMs, APIs, programmable payments, and enterprise trust layers.
- Main benefits: hyper-personalized shopping, reduced operational costs, increased conversion and order value, 24/7 customer engagement, informed decision-making.
Modern commerce is undergoing a quiet but profound transformation. From people actively shopping we are moving to software acting on behalf of people. And from obsessing over conversion optimization to delegated decision-making, where intelligent systems decide what to buy, when, from whom, and under which conditions.
This blog post explores the question “What is agentic commerce?” from multiple perspectives.
SaM Solutions offers a wide range of platform-based and from-scratch ecommerce development services that help you reach your digital sales objectives.
Defining Agentic Commerce
Agentic commerce refers to a commerce paradigm in which autonomous AI agents perform shopping-related tasks. They are guided by predefined goals, permissions, and real-time context. These agents do not merely assist users. They take initiative, make decisions, and execute transactions across platforms.
From a formal perspective, the agentic commerce definition can be summarized as follows: a system where software agents combine reasoning, memory, tool usage, and feedback to manage purchasing, negotiation, payment, fulfillment, and post-purchase engagement without continuous human input.
What makes it agentic is not intelligence alone, but a specific set of properties:
- Goals: Agents operate toward explicit objectives, e.g., cost minimization or ensuring product availability.
- Autonomy: After activation, agents decide and act without step-by-step human instructions.
- Tools: Agents invoke APIs for catalogs, pricing, payments, logistics, and CRM systems.
- Memory: Past interactions, preferences, contracts, and constraints are stored to inform future decisions.
- Feedback: Outcomes continuously refine future actions.
This distinguishes agentic commerce sharply from earlier approaches such as:
- Rule-based automation that follows predefined logic and breaks when context changes.
- Chatbots that respond conversationally but rarely execute complex, multi-step transactions.
- Recommendation engines that suggest products but rely on humans to complete the purchase.
The Evolution from Assisted to Autonomous Shopping
The evolution toward autonomous commerce mirrors a broader progression in artificial intelligence, where each layer adds both capability and business value.
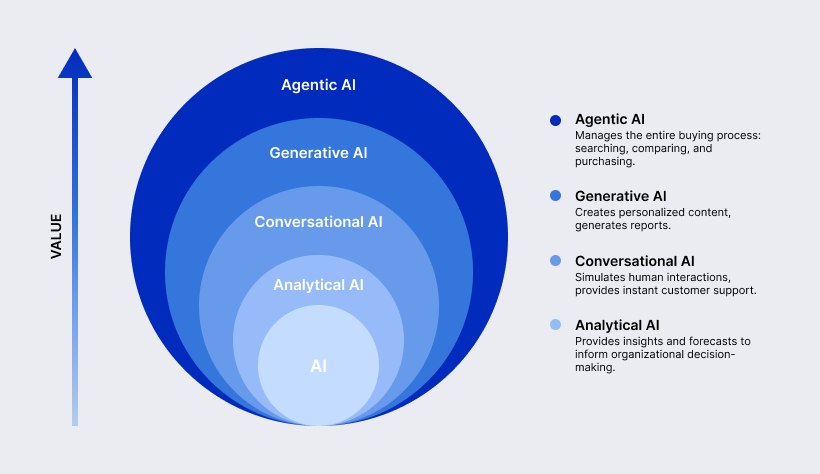
- At the foundation sits analytical AI, focused on pattern recognition, forecasting, and anomaly detection.
- On top of that, conversational AI introduced natural language interfaces, allowing users to ask questions or issue simple commands.
- Generative AI expanded this further by creating content, summaries, and recommendations tailored to individual contexts.
- At the highest level is agentic AI. Unlike earlier forms, it does not stop at analysis, conversation, or generation. Agentic AI acts. It selects options, executes transactions, resolves issues, and adapts its behavior with the time.
Each layer builds on the previous one, but only the agentic layer enables true autonomy in commerce. So, this layered progression is also reflected in how digital shopping itself has transformed.
- Early ecommerce was driven by search. Users knew what they wanted and manually looked through catalogs.
- The next stage introduced recommendation engines, which surfaced relevant products based on historical data but still relied on human decisions.
- More recently, AI copilots emerged, i.e. assistants that help compare products, configure complex offerings, or guide users through checkout.
- Agentic commerce represents the next step: autonomous execution, when the system takes responsibility for the outcome.

Autonomous commerce is gaining momentum now because four critical capabilities have matured at the same time:
- Large language models (LLMs) that can accurately understand intent and reason within complex contexts.
- APIs that give access to real business actions (not just data) across commerce, ERP, and logistics systems.
- Payment and fulfillment infrastructures that can be triggered programmatically and securely.
- Enterprise-grade trust layers for security, governance, auditability, and compliance.
For executives, the implication is straightforward: commerce is no longer limited by human attention or availability. It can scale autonomously. And unlike classic AI personalization, which only recommends and waits, autonomous systems can act.
How Agentic Commerce Functions
At an architectural level, autonomous commerce is not a single AI but a coordinated system of specialized agents. Orchestration logic determines when agents activate, how they collaborate, and where human approval is required.
User intent and agent activation
Every workflow starts with intent. This may be explicit (“reorder office supplies”) or inferred (“inventory levels dropped below threshold”). Natural language understanding translates intent into actionable objectives, so the appropriate agent or group is activated.
Independent task execution
After activation, smart programs perform tasks independently: searching catalogs, evaluating suppliers, comparing delivery terms, or scheduling purchases. Execution is asynchronous and continuous, not session-based like traditional shopping.
Intelligent product curation
Agents curate products dynamically, factoring in availability, historical performance, pricing trends, and contractual obligations. This goes beyond personalization into context-aware decision-making.
Automated merchant negotiation
To function reliably, agentic commerce requires retailers and service providers to open their systems to machine-readable access. In practice, this means offering APIs for product data, pricing, real-time availability, and key commercial policies such as returns, warranties, and fulfillment. These interfaces allow direct interaction between merchants and autonomous programs. Thus, agents can verify stock conditions and complete purchases on a customer’s behalf.
As this interaction model matures, it is increasingly framed around new standards. Currently, the Agentic Commerce Protocol(ACP) and the Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP) are in the spotlight. Such protocols standardize how merchants and AI agents exchange structured commercial information in a consistent and reliable way.
Frictionless payment processing
Payment execution is embedded directly into the workflow. Agents initiate transactions at the moment when conditions are met, integrating with ERP and financial systems for reconciliation and auditability.
Proactive customer care
Post-purchase, agents monitor fulfillment, anticipate issues, and trigger support actions proactively. Customer care shifts from reactive problem solving to continuous experience management.
Core Benefits of Agentic Systems in Commerce
Agentic commerce isn’t about trying out new AI features just for their own sake. It is valuable because it has a real effect on business.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
Like any new technology, agentic commerce introduces new risks that must be managed deliberately.
Security vulnerabilities and fraud prevention
Autonomous systems and the Model Context Protocol (MCP) expand the attack surface. That’s why companies must invest into strong authentication, encrypted communication, and transaction monitoring.
Algorithmic bias and fairness audits
Agent decisions reflect training data and objectives. Regular audits are required to prevent biased outcomes, especially in pricing and recommendations.
Integration complexity with legacy systems
Most enterprises operate heterogeneous environments, consisting of, among other things, legacy software. Integrating agentic layers with ERP, CRM, and commerce platforms requires careful API design and data normalization.
Accountability and decision ownership
A critical question arises: who is responsible for an agent’s decision? Enterprises must define approval thresholds, maintain audit logs, and ensure explainability, particularly in regulated industries.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Agentic commerce is already going beyond theory into practical applications. Its strongest use cases appear where decisions are repetitive, time-sensitive, and closely tied to operational or financial outcomes.
B2B supply chain automation
In B2B environments, supply chains are complex and sensitive to disruption. Agentic systems continuously monitor inventory levels, demand forecasts, and contractual terms. When predefined thresholds are reached, autonomous assistants can evaluate suppliers, negotiate prices within approved limits, and place orders without human participation.
| Who benefits | What gets automated | What KPI improves |
| Procurement teams, supply chain managers, and finance departments | Inventory monitoring, supplier selection, price negotiation, purchase execution, replenishment scheduling | Procurement cycle time, stock availability, cost-to-serve |
Dynamic subscription services
Subscription models depend on timing and relevance. Autonomous assistants can adjust subscription parameters based on real usage patterns, customer behavior, and contractual constraints. Instead of relying on static plans or periodic manual reviews, agents can proactively upgrade, downgrade, or renew subscriptions at the right moment.
| Who benefits | What gets automated | What KPI improves |
| Subscription-based businesses, product managers, and customer success teams | Plan adjustments, renewals, usage-based pricing decisions, retention actions | Customer lifetime value, churn rate, renewal rate |
Personalized retail experiences
In consumer retail, autonomous shopping assistants learn preferences, monitor consumption patterns, and make purchasing decisions when conditions are optimal. This reduces friction for customers and increases relevance across touchpoints. Retailers benefit from higher conversion rates and stronger loyalty, as shopping becomes not a sequence of isolated transactions but a continuous service.
| Who benefits | What gets automated | What KPI improves |
| End customers, ecommerce teams, and marketing departments | Product discovery, replenishment decisions, cross-channel purchasing, post-purchase engagement | Conversion rate, average order value, repeat purchase rate |
Autonomous travel planning
Travel planning involves multiple vendors, changing prices, and frequent disruptions. Autonomous agents are able to coordinate bookings across flights, accommodations, and services while optimizing for cost, preferences, and policy constraints. When disruptions occur, AI can rebook or adjust itineraries automatically.
| Who benefits | What gets automated | What KPI improves |
| Travelers, corporate travel managers, and travel service providers | Itinerary planning, booking coordination, price optimization, exception handling | Booking efficiency, cost savings, traveler satisfaction |
Preparing Your Business for Agentic Commerce Adoption
Adopting agentic commerce is not a one-time thing or a feature rollout. It is a journey to maturity that includes technology, process design, and changes to the organization. The technical foundation is important, but long-term success also depends on how well responsibilities are defined.
Assess organizational readiness and change management
Before introducing autonomous agents, organizations need clarity around ownership and accountability. Employees must agree on which processes can be delegated to intelligent software, where human approval is required, and how exceptions are handled. Building trust in AI-driven decisions takes time, especially in >enterprise environments. And well-defined human-in-the-loop strategies are essential to ensure adoption rather than resistance.
Audit and structure your product data
Autonomous assistants use data that should be accurate, consistent, and machine-readable. Product information, pricing logic, availability rules, and contractual terms must be structured in a way that agents can interpret and act on without ambiguity. Many organizations underestimate this step, yet data readiness determines how quickly agentic systems can move from pilot to production.
Develop a robust API strategy
In autonomous commerce, APIs are the primary execution layer. Agents interact with commerce platforms, ERP systems, payment services, and fulfillment providers entirely through interfaces. A thought-out API strategy ensures that these systems expose reliable, secure, and well-documented endpoints.
Implement agent-specific performance metrics
Traditional ecommerce KPIs capture outcomes, but they do not explain how autonomy improves performance. Agentic systems require additional metrics, such as reductions in cycle time, the share of transactions executed autonomously, and the efficiency of exception handling. These indicators provide visibility into both performance gains and operational risk.
Establish AI governance and ethics frameworks
Autonomy must be bounded by clear rules. Governance frameworks define what agents are allowed to do, under which conditions, and with what level of oversight. This includes approval thresholds, audit trails, and compliance requirements, ensuring that agentic commerce operates safely within legal, financial, and ethical boundaries.
Pilot projects with defined use cases
To succeed, organizations should begin with clearly scoped, high-impact use cases where benefits are easy to measure and risks are manageable. These pilots create learning loops, allowing teams to refine agent behavior, improve integrations, and build internal confidence before scaling autonomous commerce across the business.
Agentic Commerce vs. Traditional Ecommerce
Comparing agentic commerce with traditional ecommerce highlights why this shift is not an incremental optimization. The two models differ fundamentally in how discovery happens, how decisions are made, and how value is sustained over time.
| Dimension | Traditional ecommerce | Agentic commerce |
| Product discovery | User-driven browsing and filters | Goal-driven, active discovery by agents |
| Execution | Manual, step-by-step by the user | Autonomous, end-to-end execution |
| Pricing | Fixed or rule-based | Context-aware, dynamically negotiated |
| Customer support | Reactive and ticket-based | Proactive and continuous |
| Relationship model | Transaction-focused | Ongoing, service-oriented |
Passive catalogs against active discovery
Passive catalogs are what traditional ecommerce uses. Customers have to know what to look for and spend time finding it in order to discover new products.
Agentic commerce replaces passive discovery with active exploration. Autonomous agents continuously scan catalogs, suppliers, and channels to identify the best options based on defined goals.
Manual search compared to autonomous execution
In a normal ecommerce flow, every step, from searching to checking out, requires some actions from a person. The system does what you tell it to do, but it doesn’t take the lead. This model works, but it causes problems and delays, especially for purchases that need to be made quickly or more than once.
Agentic commerce removes this dependency on manual interaction. Once objectives and constraints are set, agents search, evaluate, and execute purchases independently. Humans remain in control through approvals and guardrails, but they are no longer required to manage every transaction.
Static pricing versus dynamic negotiation
Pricing in traditional ecommerce is typically static or adjusted through predefined rules and promotions. Negotiation, if it exists, is manual and time-consuming.
Dynamic negotiation is possible with agentic commerce. Agents look at pricing in real time, taking into account volume, timing, supplier terms, and past performance. They can negotiate and agree to the best terms automatically, as long as they stay within the limits that have been set.
Reactive support opposed to proactive service
The way traditional ecommerce works, customer service is reactive. When problems happen, they are usually fixed through support tickets or phone calls.
Agentic systems work ahead of time. Agents keep an eye on fulfillment, look for problems, and take action to fix them before they get worse. Support changes from fixing problems to stopping them from happening in the first place.
Isolated transactions and enduring relationships
In traditional ecommerce, each purchase is seen as a separate event. Even though customer data can be kept, interactions are mostly short-term and transactional.
Agents remember what the customer or organization wants, learn from the results, and always act in their best interests. This builds long-lasting relationships based on trust and relevance. This changes commerce from a series of one-time transactions into a long-term service.
The Future of Agentic Commerce
The new commerce approach is still in its early stages, but its trajectory is becoming clearer. Over the next few years, adoption will be driven by pragmatic business needs, with enterprises focusing on where autonomy delivers immediate operational and financial returns.
In the near term (12–24 months), adoption will concentrate on internal use cases. Enterprises will deploy autonomous agents within procurement, supply chain operations, pricing, and replenishment (areas where processes are well-defined and risk can be tightly controlled).
In the medium term, agentic commerce will extend beyond individual enterprises into agent-to-agent interactions. Autonomous buyers will negotiate directly with autonomous sellers, and marketplaces will increasingly be designed for machine participants. Product listings, pricing logic, and availability signals will be optimized for structured consumption by agents, not visual presentation alone.
What SaM Solutions Offers
SaM Solutions implements SAP, Emporix, and Adobe Commerce platforms that are fully prepared for the era of agentic commerce. Our approach turns traditional commerce systems into intelligent, interconnected ecosystems capable of seamless interaction with AI agents.
Conclusion
The reality is that understanding agentic commerce meaning has become essential for retailers to stay ahead in the coming years. With SaM Solutions as your technology partner, you gain future-proof commerce platforms designed to orchestrate data, processes, and services intelligently. This way, you empower your business to stay visible, relevant, and competitive in the new agent-driven digital economy.









![15 Best AI Tools for Java Developers in 2026 [with Internal Survey Results]](https://sam-solutions.com/wp-content/uploads/fly-images/18712/title@2x-6-366x235-c.webp)





